No products in the basket.
HAKKO Recommendations for Selection of Tip Size (Diameter)

Select tip shape
HAKKO Recommendations for Selection of Tip Size (Diameter)
When selecting the most suitable tip size (diameter) for the workpiece, what do you base your selection on? When soldering, if the tip shape has already been determined, then you may be at a loss to select the size (diameter). How do you select what size (diameter) to use?
If the proper size (diameter) for the workpiece is selected, the following merits will be obtained and the “soldering environment” will be improved.

- Heat will be efficiently transferred to the workpiece, which offers easy wetting by solder.
- If wetting by solder is easy, the setting temperature can be set to the lowest possible temperature.
- If the set temperature is lower, tip oxidation is prevented.
- If tip oxidation is prevented, the service life of the tip will be prolonged.
- If the service life of the tip is prolonged, the cost will be reduced!
Now, let’s study how to select a tip with the appropriate size by using the T12 series Shape D as an example.
Step 1 Select a tip with the appropriate size for the workpiece.
The size of the tip changes the contact area with the workpiece. The contact area determines how efficiently heat is transferred to the workpiece. What size will transfer heat the most efficiently? Let’s study it by using T12-D12, D16 and D24 as examples.
Look at the following Graph 1 and 2 for tips smaller than the workpiece, appropriate for the workpiece and larger than the workpiece.
Graph 1 : Change in working time due to different tip size selection
Measurement conditions
| Measurement method | Solder at 5 points and measure the time until the temperature of the workpiece reaches 250ºC. |
| Board | Glass epoxy board |
| Component | Connector |
| Tip shape | T12-D12, T12-D16 and T12-D24 |
| Temperature setting | 360ºC |
| Solder | Lead-free solder (Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu) Φ0.5 |
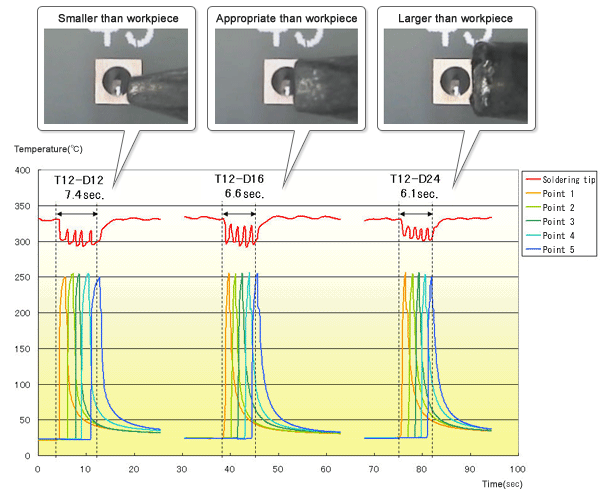
Comment It is assumed that if the drop in temperature and working time are focused on, “selection of a tip with a larger size” is favorable. The shorter working time makes the tip less oxidized, so “tip with the appropriate size” is also acceptable. Which one is better size, ‘tip with the appropriate size’ or ‘tip with the larger size’?
Graph 2 : Change in temperature of workpiece due to different tip size selection
Measurement conditions
| Measurement method | Measure the temperature of the workpiece when 5-point soldering is performed once every 3 seconds. |
| Board | Glass epoxy board |
| Component | Connector |
| Tip shape | T12-D12, T12-D16 and T12-D24 |
| Temperature setting | 360ºC |
| Solder | Lead-free solder (Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu) Φ0.5 |
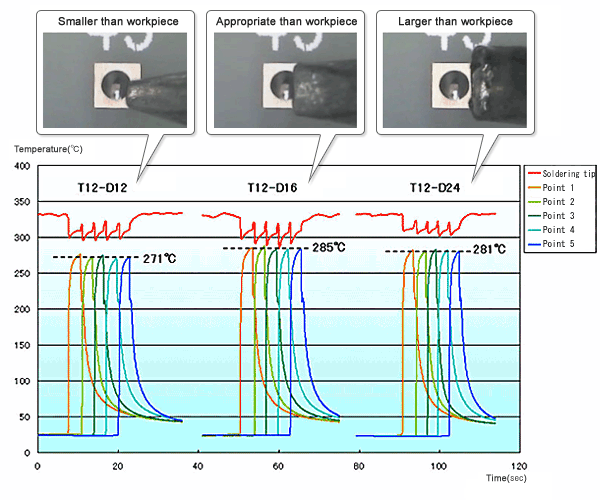
Comment
It is assumed that “selection of tip with the appropriate size for the workpiece” is better considering the temperature drop and the workpiece temperature. In the graph, the temperature drop of “tip with the appropriate size” is the largest, which indicates the sufficient heat is transferred to the workpiece. So in the end, is “tip with the appropriate size for the workpiece” better?
The two types of graphs show that there is a complicated relationship between drop in temperature, working time and temperature of the workpiece. In order to obtain the best “soldering environment”, the tip size should be determined after taking the above conditions into consideration.
Finally, which is the best selection: “smaller than the workpiece”, “appropriate for the workpiece” or “larger than the workpiece”? We recommend a tip with “the appropriate size for the workpiece”. If the tip is smaller than the workpiece, heat is not efficiently transferred and working time will be prolonged. On the other hand, if the tip is larger than the workpiece, it causes P.W.B. to be damaged.
If it is impossible to use a tip with the appropriate size for the workpiece in a narrow space, reduce the tip size gradually to minimize the amount of size reduction and solder the workpiece in combination with the following methods.
Solder the workpiece using a combination of “a tip smaller than the workpiece” and a preheater, which can preheat the P.W.B. by applying hot air to the underside of the P.W.B. SMD rework system /Jig
Replace “a tip smaller than the workpiece” with an N2 system (nitrogen gas) and solder a workpiece. The preheating effect of the nitrogen gas will increase the wettability and ductility.
| – Smaller than the workpiece | |
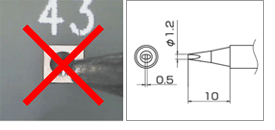 | A tip smaller than the workpiece connot transfer sufficient heat to the workpiece. If the tip is smaller than the land, heat from the tip is not transferred to a workpiece efficiently and it takes much time to transfer a sufficient amount of heat that solder can be wet. * The reason for the temperature drop being the smallest is because heat cannot be transferred to the workpiece efficiently. |
| – Appropriate for the workpiece | |
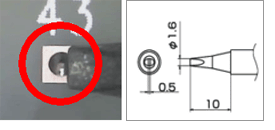 | A tip with the appropriate size for the workpiece can tranfer heat to the workpiece efficiently. If the tip size is appropriate for the land, an amount of heat sufficient to let solder be wetted is transferred, and the drop in temperature will be larger. However, if a soldering iron with excellent thermal recovery rate is used, the time until recovery to the set temperature is shortened, enabling the working time to be reduced as a result. |
| – Larger than the workpiece | |
 | Do not use a tip larger than the workpiece. Doing so may cause the P.W.B. to be damaged. |

